Understanding Stomach Gurgling After Eating
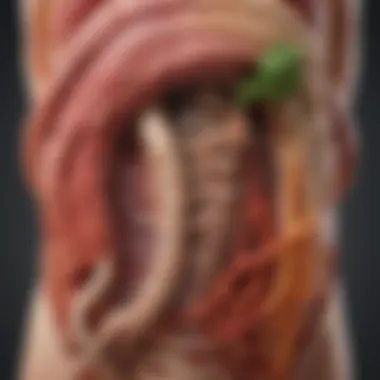

Intro
Stomach gurgling after eating is a common concern that many individuals experience at various points in their lives. This sound, often referred to as borborygmi, occurs when gas and fluid move through the intestines. While many dismiss it as a trivial annoyance, understanding its mechanisms, dietary influences, and potential health implications is essential for better digestive health.
This article seeks to delve into the intricacies surrounding stomach noises that can follow a meal. By exploring the gastrointestinal anatomy and the physiological factors at play, we can uncover what causes this phenomenon, highlighting specific types of foods and eating behaviors affecting digestive sound production. Furthermore, we will discuss instances when gurgling may signal a need for medical consultation, providing clarity and actionable insights for anyone concerned about their digestive well-being.
Intro to Stomach Gurgling
Stomach gurgling, often referred to as borborygmi, serves as an auditory signal of internal digestive processes. Understanding the significance of these sounds is key to grasping how our digestive system functions. Not merely a cause for mild embarrassment, gurgling can offer insights into dietary habits, digestive health, and the efficiency of our gastrointestinal tract. Hence, exploring this topic provides immense value.
This section aims to underline essential aspects concerning stomach gurgling, including its nature, the physiological processes behind it, and its meanings in the context of post-meal experiences.
Definition and Description
Stomach gurgling refers to the rumbling sounds produced by the movement of food, liquid, and gas through the intestines. These sounds typically occur when the stomach is empty or after eating. The noise is generated during peristalsis, the process through which the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract contract and relax to propel contents forward. The intensity and frequency of these sounds can vary based on several factors. It is vital to recognize that while gurgling is common and usually harmless, it might also indicate an underlying condition in some cases.
Common Misconceptions
Many misconceptions surround stomach gurgling, often leading to unnecessary anxiety about digestive health. Some individuals assume that gurgling sounds are directly related to hunger. In reality, while these sounds may increase when hungry, they are largely made regardless of whether one has eaten recently. Another common belief is that loud gurgles suggest a serious health issue. However, it is quite typical for gurgling to occur after meals as the body processes food.
Moreover, some think that the presence of gurgling noises means one has an excess of gas. Although gas production can contribute to these sounds, a variety of factors also play a role. It is important to differentiate between normal digestive sounds and those that may signal a need for medical assessment. A better understanding of these aspects can help demystify stomach gurgling and promote a more informed approach to digestive health.
The Anatomy of the Digestive System
Understanding the anatomy of the digestive system is crucial for comprehending the causes of stomach gurgling after eating. This system plays a vital role in breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and delivering waste products from the body. Knowledge of how each organ functions independently, yet collectively contributes to digestion, enhances our understanding of these digestive sounds.
Overview of Gastrointestinal Organs
The gastrointestinal tract comprises various organs that work together to digest food. It begins with the mouth, where food is mechanically broken down. Next, the esophagus transports food to the stomach through muscle contractions known as peristalsis. Here are the main organs involved:
- Mouth: Initiates digestion by breaking down food with teeth and saliva.
- Esophagus: A muscular tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach.
- Stomach: A hollow organ where food is mixed with digestive juices.
- Small Intestine: The primary site for nutrient absorption.
- Large Intestine: Absorbs water and forms waste for elimination.
Each organ has distinct functions, influencing how food gurgles within the stomach as it transitions through the digestive process.
Role of the Stomach and Intestines
The stomach and intestines have specific responsibilities in digestion. The stomach acts as a reservoir that temporarily holds food after eating. Here, enzymes and acids break down food further, leading to the formation of a semi-liquid substance called chyme. This process is crucial for adequate nutrient absorption later in the digestive pathway.
The small intestine, which follows the stomach, continues the digestion of food using enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver. This organ is responsible for absorbing most nutrients and plays a significant role in regulating digestive sounds.
It is important to note that sounds in the digestive system often reflect its functioning status.


Various factors can trigger increased gurgling sounds, including the types of food consumed and digestive health. The anatomy of the digestive system is not merely academic; it is deeply intertwined with our daily experiences of eating and digestion. Understanding these elements can lead to better dietary choices and improved digestion.
Mechanisms of Stomach Sounds
Understanding the mechanisms that cause stomach sounds is crucial for comprehending how our digestive system operates. Stomach gurgling is a complex phenomenon that results from several physiological processes. Knowing the underlying mechanisms can help individuals make informed choices about diet and eating habits.
Peristalsis: The Movement of Food
Peristalsis refers to the series of wave-like muscle contractions that transport food along the digestive tract. This process is vital for moving food from the esophagus to the stomach and eventually into the intestines. Peristalsis is triggered by the presence of food, stimulating smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract to function in a coordinated motion.
The movement of food through the digestive system promotes mixing and breakdown, essential for digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Importance of Peristalsis:
- Enhances Digestion: Facilitates the grinding and mixing of food with digestive juices.
- Aids Nutrient Absorption: Optimizes conditions for allowed nutrients to pass into the bloodstream.
- Prevents Bloating: Regular contractions help push gas and food residues, minimizing discomfort.
When peristalsis is disrupted, it can lead to abnormal gurgling sounds. This could be a sign of gastrointestinal issues or dietary missteps.
Gas Production and Release
Gas in the stomach and intestines originates from various sources, including swallowed air, the breakdown of certain foods, and bacterial fermentation. Ingredients like beans, cruciferous vegetables, and dairy can produce significant amounts of gas. When food is digested, gas accumulates and may be expelled as burps or flatulence.
This process can lead to audible stomach gurgling, particularly after consuming significant quantities of gas-producing foods.
- Key Points About Gas Production:
- The role of bacteria: Gut flora helps break down food, resulting in gas release.
- Swallowed air: Eating quickly or talking while eating increases swallowed air, which can amplify sounds.
- Cooking methods: Frying or boiling can influence gas formation; for example, beans may produce more gas when cooked improperly.
These mechanisms are essential to understand not only for recognizing normal digestive sounds but also to identify when gurgling may indicate a dietary problem or underlying health issue.
Factors Influencing Gurgling Sounds
Stomach gurgling, or borborygmi, is influenced by various elements that merit attention. Understanding these factors enhances awareness about digestive health and allows individuals to make informed dietary choices. The elements discussed in this section—type of food consumed, eating speed and meal timing, as well as hydration—play significant roles in the sounds produced by the gastrointestinal system.
Type of Food Consumed
The foods one eats can substantially affect the occurrence of stomach gurgling. Fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, might create more gas as they are processed in the intestines. This is due to their complex carbohydrate structure, which requires fermentation by gut bacteria. While fiber is beneficial for digestion, an excessive intake can lead to increased gurgling sounds.
Moreover, dairy products can lead to gurgling, especially among individuals with lactose intolerance. In such cases, the absence of the enzyme lactase leads to unprocessed lactose in the gut, leading to fermentation and gas development, which results in audible stomach sounds. It's prudent to be mindful of carbonated beverages too; they introduce gas directly into the digestive system, often heightening gurgling and bloating after consumption.
Eating Speed and Meal Timing

The manner in which food is consumed is crucially linked to digestive sounds. Eating too quickly can result in swallowing air, which contributes to gas formation in the digestive tract. This can exacerbate gurgling, as the body attempts to expel the excess air. Taking time to chew food thoroughly promotes better digestion and reduces the risk of over-accumulating gas.
Meal timing also holds importance. Eating at irregular intervals may disrupt the natural rhythmic contractions of the stomach and intestines. As hunger builds, the digestive system becomes more active, sometimes resulting in noticeable sounds as it prepares for food intake. Regular meal patterns help maintain digestive stability and minimize unexpected gurgling.
Hydration and Stomach Sounds
Hydration plays a significant role in digestive health and can influence gurgling sounds. Adequate water intake is essential for the digestive system to function correctly. Water helps in breaking down food and facilitates smoother passage through the gastrointestinal tract. Dehydration can lead to constipation and reduced digestive efficiency, causing more pronounced sounds as the body struggles to process food.
Conversely, drinking large quantities of liquids during meals can also trigger increased gurgling. The presence of excess liquid alongside solid food can create a sloshing effect in the stomach, enhancing the sounds produced. Finding a balance in beverage consumption can aid in creating a more harmonious digestive environment.
In summary, understanding these influencing factors empowers individuals to make healthier choices and mitigate unwanted stomach gurgling.
Common Dietary Factors
Understanding common dietary factors is essential in unraveling the causes of stomach gurgling. Food choices directly influence digestive processes, which can manifest as gurgling sounds. By delving into various food elements, one can appreciate their specific effects on the gastrointestinal system. This section focuses on three important food categories: fiber-rich foods, dairy products, and carbonated beverages. Each plays a unique role in digestive sounds and processes.
Fiber-Rich Foods and their Effects
Fiber-rich foods are well-known for their health benefits. They aid in digestion and promote regular bowel movements. Foods like oats, beans, and fruits contain soluble and insoluble fiber. The intake of whole grains can enhance gut health, but it also can lead to increased gurgling sounds. This happens due to the fermentation of fiber in the intestines. As bacteria break down fiber, gas is produced, contributing to the audible sounds. Additionally, a sudden spike in fiber intake can cause distress for the digestive system if the body is not used to it. Gradually incorporating fiber-rich foods into daily meals is advisable to prevent excessive gurgling.
Dairy Products and Lactose Intolerance
Dairy products are significant dietary factors that can lead to stomach gurgling for those with lactose intolerance. Lactose, the sugar found in milk and dairy, can be difficult to digest for some individuals. Symptoms of lactose intolerance include bloating, abdominal pain, and gurgling sounds. When lactose is not properly broken down, it ferments in the intestine, resulting in gas and noise. Cheeses and yogurt often contain lower lactose amounts, making them easier to digest, but the effects vary among people. It is beneficial to monitor dairy consumption and consider lactose-free options if symptoms occur.
Carbonated Beverages and Gas Formation
Carbonated beverages are another crucial dietary factor that can lead to stomach gurgling. The bubbles in sodas and sparkling water are composed of carbon dioxide gas. When consumed, this gas enters the digestive tract, leading to sensations of bloating and creating gurgling sounds. The acid in these drinks can also irritate the stomach lining, compounding any potential discomfort. Reducing intake of carbonated beverages can lessen gurgling and provide relief. Choosing still water or non-carbonated drinks may be more advisable for individuals who experience these symptoms frequently.
"Being mindful of food choices is key in managing digestive sounds, which often indicate how well the body handles certain ingredients."
Medical Conditions Related to Gurgling Sounds
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Gastrointestinal disorders often manifest with a variety of symptoms, including gurgling sounds. Conditions such as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn's disease may lead to unusually loud and frequent stomach noises. In IBS, for instance, the intestines may be overly responsive due to various triggers, leading to increased peristalsis. This heightened activity can result in pronounced gurgling, especially after meals.
The importance of identifying these disorders cannot be overstated. Many people can manage their symptoms through dietary adjustments or medication if they understand the root causes behind their gurgling sounds. Additionally, an accurate diagnosis may lead to more serious conditions being ruled out. It promotes timely intervention, which is vital in preventing further complications.
Understanding gastrointestinal disorders is crucial as they can sometimes lead to more severe health issues if left unchecked.
Food Allergies and Sensitivities


Food allergies and sensitivities can also contribute to stomach gurgling after eating. They can provoke an imbalance in the digestive system. When a person with lactose intolerance consumes dairy, for example, their body struggles to digest lactose. This can lead to excessive gas production and subsequent gurgling noises. Similarly, gluten intolerance can cause similar symptoms as the body reacts to gluten-containing foods.
For individuals suspecting food allergies, keeping a food diary may be helpful. Noticing patterns in gurgling sounds in relation to certain foods can provide insight into possible sensitivities. Consulting a healthcare professional for testing is advisable if food allergies are suspected, as managing these can significantly improve overall comfort and digestive health.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Determining the right moment to seek medical help regarding stomach gurgling is crucial, especially when it impacts quality of life. While occasional gurgling is typically benign, persistent or severe symptoms may indicate an underlying issue that warrants professional evaluation. This section elaborates on important considerations when it comes to seeking medical advice.
Identifying Concerning Symptoms
To decide when medical consultation may be necessary, it is important to recognize concerning symptoms related to stomach gurgling. Some signs to pay attention to include:
- Persistent Pain: If stomach gurgling is accompanied by sharp or persistent abdominal pain, this may signal a more serious condition.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Sudden weight loss that is not attributed to diet change or increased activity can be alarming and requires evaluation.
- Change in Bowel Habits: Any significant alteration in bowel habits such as diarrhea or constipation, particularly when accompanied by gurgling, can signify issues that need to be addressed.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Frequent nausea or vomiting alongside gurgling may indicate a gastrointestinal obstruction or infection.
- Fever: A rise in body temperature accompanying gastrointestinal symptoms often suggests infection and should be checked by a doctor.
- Blood in Stool: The presence of blood signals potentially serious gastrointestinal disorders that should be investigated immediately.
Recognizing these symptoms will help in distinguishing typical digestive sounds from those suggesting a need for medical evaluation.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals
After identifying worrying symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional becomes essential. A medical expert can conduct necessary assessments to determine the underlying cause of the gurgling sounds. During a consultation, you can expect the following:
- Thorough History Taking: The healthcare provider will inquire about your medical history and any related symptoms to understand the context of your concerns better.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination can reveal clues about the health of your digestive system. The doctor may palpate your abdomen to check for tenderness or distension.
- Diagnostic Tests: Depending on findings, tests such as blood tests, imaging scans, or endoscopy may be recommended to identify any underlying conditions or disorders.
It is advisable not to delay seeking professional help when concerning symptoms arise. Timely medical attention can address potential issues early, promoting overall health and digestion.
"Ignoring symptoms can lead to more serious health issues. Seeking advice early on is wise for your digestive health."
Preventative Measures and Dietary Adjustments
Understanding how to manage stomach gurgling after eating is crucial for maintaining digestive health. It is not just about alleviating the sounds that occur post-meal, but about fostering an environment in which digestion can proceed smoothly and comfortably. Here, we explore several preventative measures and dietary adjustments that can contribute to overall gastrointestinal well-being.
Mindful Eating Practices
Mindful eating is essential to prevent excessive stomach sounds. This approach encourages individuals to pay attention to their eating habits. Eating slowly helps the body adequately digest food without overwhelming the stomach. Often, people rush through meals, leading to excessive air intake. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Chew Thoroughly: Chewing food well slows down the eating process and aids in digestion. This allows digestive enzymes in saliva to start breaking down food before it even reaches the stomach.
- Limit Multitasking: Focusing solely on eating can improve awareness of food intake and portion sizes. Avoid distractions like smartphones or television during meal times.
- Recognize Hunger Cues: Understanding when you are truly hungry can prevent overeating, which contributes to stomach gurgling. It is important to listen to your body.
By practicing mindful eating, individuals can reduce the chances of overeating and, consequently, lessen the likelihood of stomach gurgling.
Adjusting Food Choices
The types of food consumed have a direct impact on digestive sounds. Certain foods can contribute to gurgling and discomfort after meals. Adjusting dietary choices can thus be very beneficial. Here are some food-related considerations:
- Reduce Gas-Producing Foods: Foods like beans, lentils, and cruciferous vegetables are known to produce gas during digestion. While they are healthy options, limiting their intake may help reduce stomach noises.
- Opt for Low-Fiber Foods: In situations where excessive gurgling occurs, consider eating low-fiber foods more frequently, as they may be easier to digest. Foods like white rice, bananas, and applesauce can be gentler on the digestive system.
- Avoid High-Sugar Foods: Sugary foods can also lead to increased fermentation in the gut, which may contribute to stomach sounds. Opting for complex carbohydrates can provide sustained energy without triggering excessive gas.
"Food is not just fuel; it's information. It talks to your DNA and tells it what to do." - Dr. Mark Hyman
Taking proactive measures in our eating habits can lead to significant changes in how our body processes food.







